DeFi or decentralized finance is the up-and-coming financial technology founded on secure distributed ledgers that resemble the ones that cryptocurrencies use.
The Federal Reserve and Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States define the specific rules for the centralized financial institutions such as brokerages and banks that consumers often turn to for direct access to financial and capital services.
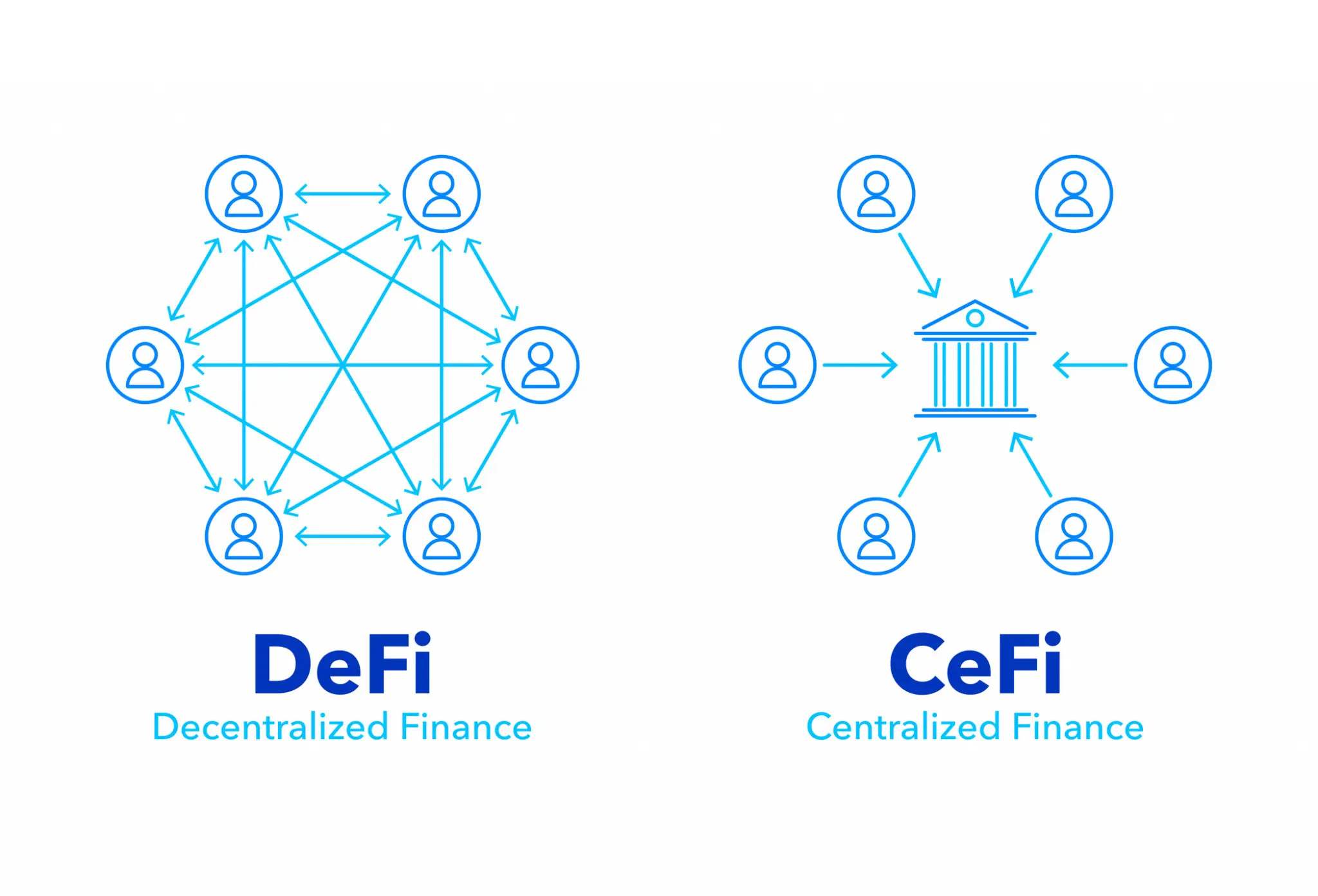
The main differences between DeFi and CeFi
DeFi: Is It Definitely for Everyone?
To challenge the centralized financial system, DeFi empowers people with the peer to peer digital exchanges. With DeFi, it gets rid of the fees that banks as well as other financial companies charge every time you use their services. Users can hold their money in a secure and safe digital wallet, transfer funds in a matter of minutes, and make the most out of DeFi as long as they have an internet connection.
Decentralized Finance vs. Centralized Finance: What’s the Difference?
Decentralized finance is different from traditional centralized banking and financial institutions.
With centralized finance, third parties and banks hold the money and facilitate its movement between the parties involved. Each one of them also charges fees for the use of their services. The credit card charge begins from the bank and then moves to the acquiring bank which will then forward the card information to the credit card network.
This network will then clear the charge and request the bank for the payment. All the entities in the chain will receive payment for their services, typically since merchants are required to pay using debit and credit cards.
Every financial transaction is overseen by centralized finance, starting from applications for loans to the services of a local bank. Two of the major goals of DeFi are to cut down transaction times and increase financial service access.
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Centralized Finance (CeFi) | |
| Authority | Control is distributed among participants, typically through blockchain technology. | Central authority (like a bank or government) controls the system. |
| Access | Anyone with an internet connection and cryptocurrency wallet can participate, regardless of location. | Often requires identification verification and can be limited based on location or financial status. |
| Transparency | Typically very transparent due to the open nature of blockchain. All transactions can be audited. | Varies. Some institutions are highly transparent while others are not. Detailed auditing can be limited. |
| Intermediaries | Designed to remove middlemen, enabling peer-to-peer transactions. | Often require intermediaries such as banks, brokers, or payment processors. |
| Speed & Efficiency | Transactions can be fast due to the absence of intermediaries, but sometimes slow and expensive due to network congestion. | Speed can be instant within the same institution but international transfers can take days. |
| Security | Relies on cryptographic security, smart contract code correctness. Risk of hacks due to smart contract vulnerabilities. | Relies on institutional security measures. Risk of internal fraud or external hacking. |
| Regulation | Mostly unregulated. | Heavily regulated by governmental bodies, offering some degree of customer protection. |
| Interest Rates | Can offer higher interest rates through mechanisms like staking & farming. Rates can be volatile. | Typically lower interest rates, set and regulated by institutions. More stable. |
| Financial Services | Lending, borrowing, staking & farming, decentralized exchanges, insurance, and more, all programmatically executed through smart contracts. | Lending, borrowing, exchanges, insurance, and more, executed by institutions. |
On the other hand, decentralized finance gets rid of intermediaries as it allows businesses, merchants, and people to use emerging technology to conduct financial transactions. DeFi uses hardware advancements, software, connectivity, and security protocols through peer-to-peer financial networks.
As long as there is an internet connection, people can borrow, lend, and trade using software that will record and verify the financial actions in the distributed financial database. The distributed database can be accessed from different locations because it accumulates and amasses data from every user and verifies it using a consensus mechanism.
Decentralized finance also eliminates the need for the centralized finance model though allowing anyone to use the financial services no matter where or who they are. Thanks to DeFi applications, users are given better control over their money using trading services and personal wallets that cater to individual users.
DeFi, however, doesn’t offer full anonymity. Transactions don’t include the name of the individual but can be traced by entities that have access to them, such as governments, as well as laws to safeguard the financial interests of an individual.
How DeFi Works
DeFi uses the same blockchain technology used by cryptocurrencies. Blockchains are secured and distributed ledgers or databases. Applications known as dApps are used for handling transactions and running the blockchain.
Transactions in the blockchain are recorded in blocks with other users verifying them. If the transaction is agreed upon by the verifiers, the block will be closed and encrypted. A new block will be formed with the data of the previous block in it.
Blocks are chained together using the data in every proceeding bloc, which explains its name blockchain. The details in the earlier blocks are unchangeable without any effects on the blocks that follow. It means that a blockchain cannot be altered in any way. This concept together with other protocols for security is responsible for a blockchain’s secure nature.
Uses and Applications of DeFi
One of DeFi’s core premises is peer-to-peer or P2P financial transactions. In a P2P DeFi transaction, two parties will agree to exchange cryptocurrency for services or goods without any third party involved.
P2P can meet the loan needs of an individual in DeFi, with the algorithm matching peers that agree on the term of the lender. A loan will be issued afterward. P2P payments are made over a dApp or decentralized application and follow a similar process in the blockchain.
The following are possible with DeFi:
- Accessibility
As long as there is an internet connection, anyone can access DeFi platforms, with transactions taking place without geographic restrictions.
- Autonomy
Decentralized finance platforms are not reliant on centralized financial institutions. They are also not subject to bankruptcy or adversity. DeFi protocols’ decentralized nature helps mitigate most of this risk.
- High-interest fees and low fees
DeFi allows any two parties to have a direct negotiation of interest rates as well as lend money using DeFi networks.
- Transparency and security
Published smart contracts on a blockchain and completed transaction records are available for everyone to check and review without revealing their identity. Since blockchains are immutable, there is no way you can change them.
Peer-to-peer lending under decentralized finance doesn’t mean that no fees and interests are involved. But it means that you will have more choices because it doesn’t matter where the lender is located in the globe.
Pros and Cons of DeFi
Here are the top benefits of decentralized finance:
- With decentralized apps, people can transfer capital all over the world.
- A high level of security is guaranteed.
- Investors can generate income.
Meanwhile, some of its drawbacks include the following:
- DeFi is often associated with a high level of volatility.
- There is an increased risk of scams and fraud.
- It can be complex to participate in DeFi not to mention that it’s also difficult to understand.
What to Expect Next?
History of DeFi
DeFi or decentralized finance is an up-and-coming financial technology that is trying to challenge the existing centralized banking system. With the help of DeFi, it eliminates the fees being charged by banks and other similar financial companies for the use of their services. It also promotes the use of P2P or peer-to-peer transactions. Thus, it will be safe to say that decentralized finance will soon become bigger and better in the near future.


 6 mins read
6 mins read