Let me introduce you to Blockchain!
Blockchain is an awesome technological invention that transformed our concept of data storage and transfer.
Now, imagine an incorruptible, decentralized, and public ledger. This is precisely Blockchain, a form of distributed database that sustains an everlasting, untamperable log of transactional data.
Consider this analogy - each transaction, or piece of data, is a block. These blocks are all linked together, forming a chronological chain - named a 'blockchain'. What sets it apart is its inherent transparency.
The data is shared and synchronized across numerous computers (known as nodes), ensuring that all participants agree on the transactions, thereby mitigating any single point of failure.
The result? An unparalleled level of security, immutability, and efficiency in recording and verifying transactions.
How Does Blockchain Work?
You're probably wondering how this groundbreaking technology operates. Well, it's a harmonious blend of cryptography, distributed consensus mechanisms, and network protocols.
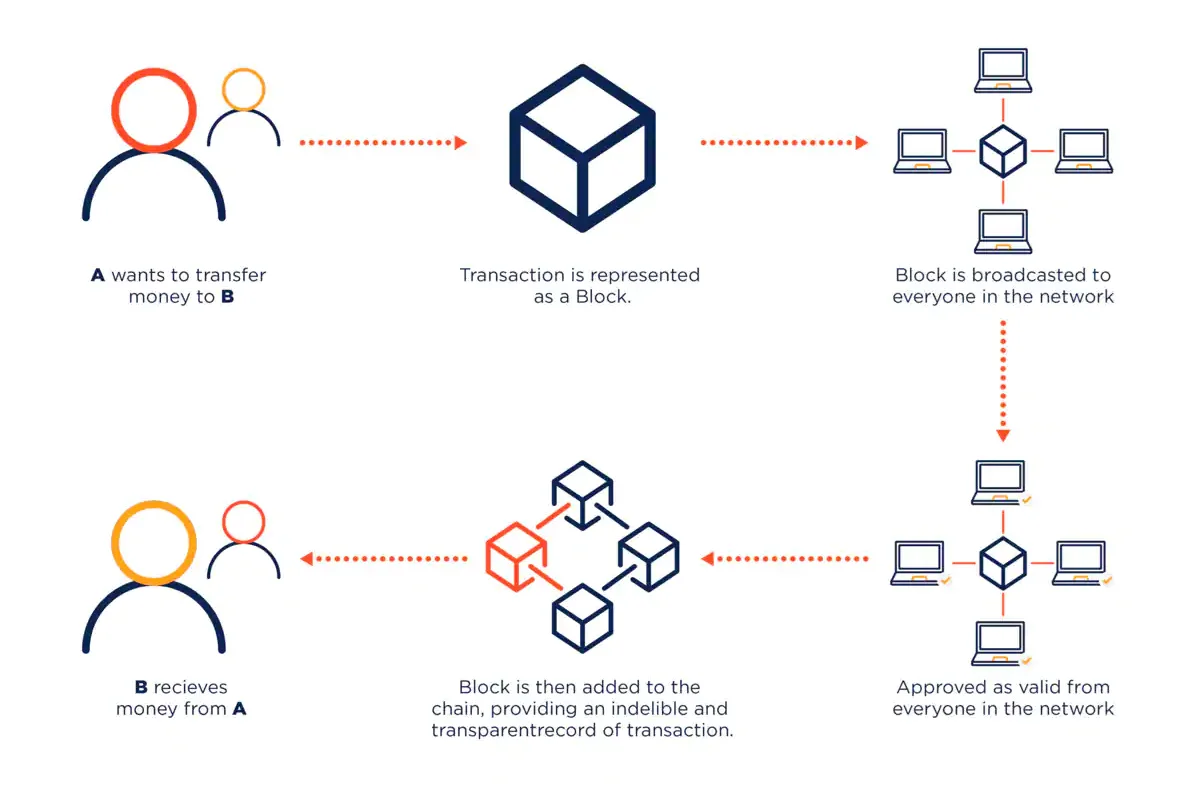
How cryptocurrency transaction works
Each time a transaction or data entry is effected on a blockchain, it is batched together with other transactions to compose a block. But this block isn't just haphazardly thrown into the chain. It first undergoes a rigorous validation process.
This validation process is carried out by network participants, known as miners or validators. This generally involves cracking sophisticated mathematical problems or attaining an agreement via specific algorithms, namely Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
Once validated, the block is added to the chain, and the information is permanently recorded, visible to all participants. The lack of a central controlling entity makes the data secure, transparent, and resistant to tampering.
But What Makes Blockchain So Viral?
Here are some interesting and fun facts about blockchain:
1. Market Size and Growth: The blockchain industry's market worth was $4.9 billion in 2021, with a forecast to catapult to $67.4 billion by 2026, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate of 68.4%. This industry is experiencing rapid growth.
2. Transaction Volume: Blockchain technology has managed and distributed more than $270 billion in transactions. By the end of 2017, approximately 300 million blockchain transactions had been processed.
3. Potential Cost Savings: According to a survey by Accenture Consulting, eight banks estimated that the potential savings on a cost base of $30 billion through the use of blockchain technology could exceed $8 billion.
4. Cryptocurrency Adoption: El Salvador became the first country in the world to adopt Bitcoin (BTC) as a legal tender. This move aims to foster financial inclusion, innovation, tourism, and overall economic development.
5. Mining and Bitcoin: Bitcoin mining involves adding new BTC transactions to the blockchain, and it is estimated that the last Bitcoin will be mined in the year 2140. To date, nearly 18 million Bitcoins have been extracted from mining.
6. Hash Rate: The hash rate refers to the processing power of a blockchain network, measured in the number of hash operations per second. For example, a hash rate of 10 TH/s means that the network performs 10 trillion calculations per second.
7. Blockchain Characteristics: A blockchain allows data in a database to be distributed among several network
8. nodes or computers. This distributed nature enhances security and eliminates the need for a central authority.
Public Blockchains vs Private Blockchains
The world of blockchain isn't just black and white. We've got two distinct types - Public and Private Blockchains.
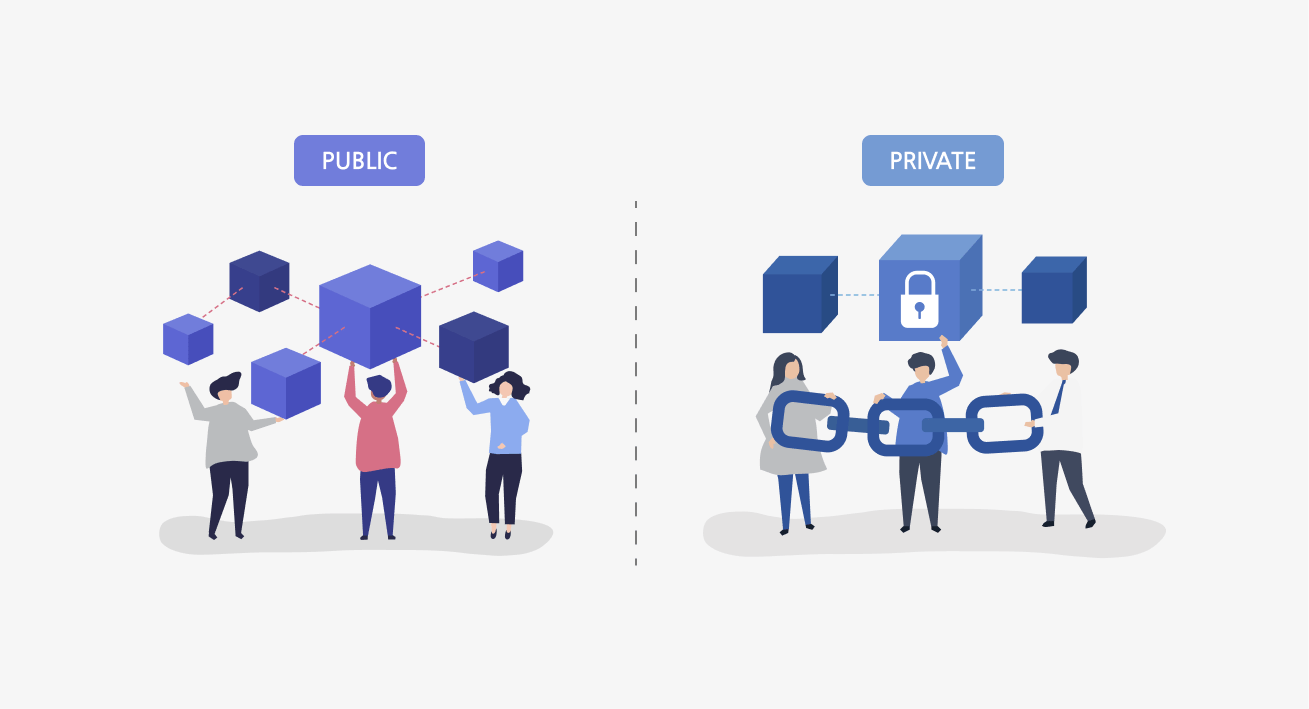
Public Blockchains
Think of public blockchains as an open book. They're permissionless, meaning anyone can read and write data. Networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on public blockchains. Here, the network is maintained by nodes that collectively agree on transaction validity.
Their hallmarks are decentralization and transparency, which require resource-intensive processes like mining. Ideal for applications valuing openness and immutability, such as cryptocurrencies and decentralized apps (DApps).
Private Blockchains
In contrast, private blockchains are more like secret diaries. Access and participation are limited to a particular group, making them perfect for businesses requiring greater control, privacy, and scalability. Unlike their public counterparts, private blockchains lean on a select group of nodes or validators for transaction validation.
They offer faster transaction processing and efficient consensus mechanisms, since incentivizing anonymous participants isn't required. Private blockchains are best for scenarios where participants trust each other and need more control over network operations, such as supply chain management and interbank transactions.
How Is Blockchain Used?
Let's talk about use-cases. Blockchain's potential stretches far beyond cryptocurrencies. It's made a significant impact on numerous sectors.
Cryptocurrencies and Financial Transactions
Yes, cryptocurrencies are the most well-known application of blockchain. It's the bedrock technology enabling secure and transparent transactions, removing intermediaries, and providing a tamper-proof transaction record.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can revolutionize supply chain transparency by securely recording and tracking goods, verifying authenticity, and ensuring regulatory compliance. This can drastically reduce fraud, counterfeiting, and inefficiencies.
Identity Management
Blockchain can be leveraged for secure and decentralized identity management, empowering individuals to control their personal data and selectively share it with trusted entities. This can bolster privacy, reduce identity theft, and streamline verification processes.
Smart Contracts
Meet the new-age contract - the smart contract. Encoded on the blockchain, these self-executing contracts have predefined rules and conditions. When conditions are met, they execute actions and facilitate asset exchange. They can automate and streamline business processes like insurance claims, real estate transactions, and supply chain agreements.
Healthcare
Blockchain can bolster healthcare data interoperability, secure patient records, and streamline medical data sharing. This improves data integrity, privacy, and consent management.
Companies That Already Used Blockchain
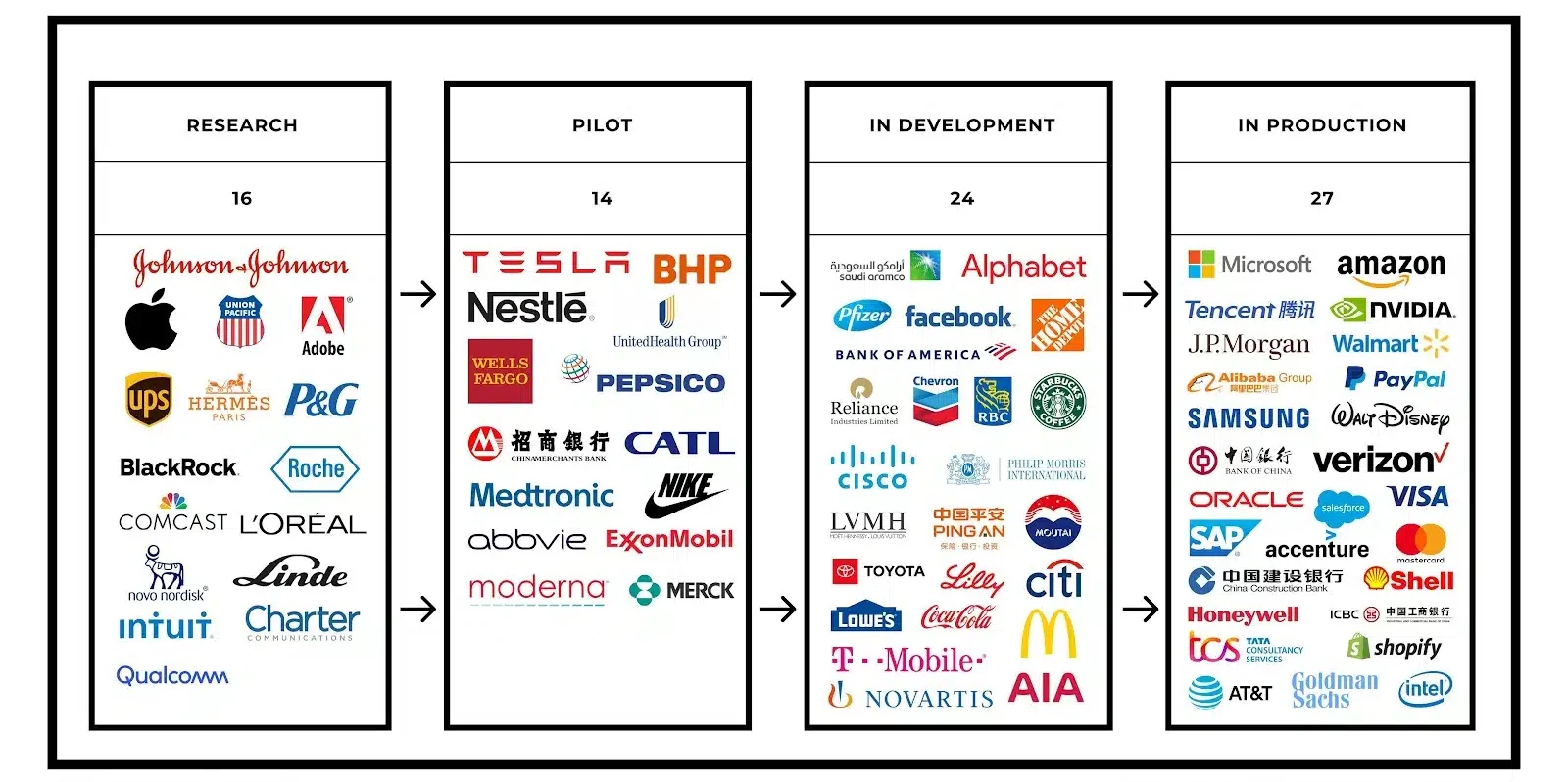
81 of the Top 100 Public Companies are using blockchain technology
Some reputable companies have already adopted blockchain technology for an array of purposes. Here are some examples:
- FedEx: FedEx, one of the world's largest logistics management companies, has embraced blockchain technology to improve supply chain transparency and efficiency.
- Burger King Russia: Burger King Russia introduced its own cryptocurrency token called WhopperCoin, which customers could use for rewards and purchases within the Burger King ecosystem.
- IBM: IBM is actively involved in blockchain implementation across different industries, including shipping, banking, healthcare, and food safety. Their solutions ingeniously marry blockchain, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence technologies.
- Shell: Shell, a major energy company, has been exploring blockchain technology for the energy sector. They have partnered with Sinochem Energy Technology Co Ltd and Macquarie to develop blockchain-based solutions for crude oil trading.
- Mizuho: Mizuho, a prominent bank, has successfully completed trade finance transactions using blockchain technology. They aim to continue leveraging the benefits of blockchain for secure data sharing and document management.
- Singapore Airlines: Singapore Airlines utilizes blockchain technology to offer loyalty-based promotions to its customers through its KrisPay app. The technology enhances the airline's customer loyalty program.
- Brookfield Asset Management: Brookfield Asset Management plans to integrate blockchain technology into its systems to reduce transaction costs and automate contracts. The company aims to leverage the benefits of blockchain for more efficient operations.
These examples illustrate how companies across varied sectors like logistics, finance, energy, and aviation have incorporated blockchain technology to optimize processes, escalate transparency, and propel innovation.
Advantages of Blockchain
Let's delve into why blockchain is causing such a stir:
Security
With cryptographic algorithms and decentralization, blockchain ensures data security and integrity. Transactions become nearly tamper-proof once recorded, offering robust protection against fraud and unauthorized modifications.
Transparency
Blockchain's transparent nature enables all participants to view and verify transactions, fostering trust and reducing the need for intermediaries.
Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and manual processes, blockchain enables faster and more efficient transactions. It reduces overheads, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Traceability
Blockchain's immutability and transparency offer comprehensive transaction and asset traceability. This is particularly useful in supply chain management, allowing tracking of goods from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and reducing counterfeiting.
Decentralization
Blockchain functions on a distributed network of nodes, which eliminate reliance on a central governing body. This enhances resilience, censorship resistance, and fault tolerance.
Disadvantages of Blockchain
Blockchain isn't perfect. Here are a few limitations:
Scalability
The requirement to store a complete blockchain copy on every node and consensus mechanisms can result in scalability issues. As the number of transactions and participants grows, the network may face limitations in transaction processing speed and storage capacity.
Energy Consumption
Particularly for Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains, significant energy consumption is a concern. The environmental impact has raised questions about the sustainability of blockchain technology.
Regulatory and Legal Challenges
The evolving regulatory framework around blockchain presents legal challenges related to data privacy, jurisdiction, and smart contract enforceability. Compliance with prevailing laws and regulations can be challenging.
Complexity
Implementing blockchain technology into existing systems can be complex and require technical expertise. Developing and maintaining blockchain networks often require specialized skills and resources.
How to Invest in Blockchain
For the investors among us, here's how to invest in blockchain technology:
Cryptocurrencies
One way is by buying cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin or Ethereum. They serve as a representation of value on blockchain networks and have gained traction as investment assets.
There are several reputable websites where you can buy cryptocurrencies. Some notable options include:
- Coinbase: Coinbase is a well-known platform> I bet you already know it! This website enables you to purchase, keep, and sell various cryptocurrencies. That includes Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more. They offer user-friendly interfaces and secure storage for your digital assets.
- Blockchain: Blockchain.com is a trusted platform for buying and selling cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. They provide a user-friendly experience and offer secure storage, trading, and swapping services.
- Crypto.com: Crypto.com is a platform where you can buy and sell over 250 cryptocurrencies using bank transfers or credit/debit cards. They accommodate multiple fiat currencies and proffer an assortment of crypto-related goods and services.
- Okcoin: Okcoin is a secure cryptocurrency exchange. For sure! They have Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dogecoin, and other cryptocurrencies for you to invest on. They also offer a feature called Okcoin Earn, where you can earn crypto rewards.
Blockchain Stocks and ETFs
Invest in companies directly involved in blockchain development or offering blockchain-related services. Some publicly traded companies and ETFs focus on blockchain and cryptocurrency-related ventures.
Venture Capital and Startups
You can finance blockchain startups via venture capital or through initial coin offerings and initial exchange offerings. However, this carries higher risks and requires due diligence.
Types of Blockchain
There are primarily three types of blockchains:
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are unrestricted and permissionless networks open for everyone's participation. They are decentralized, free from any central authority's control over the network. Public blockchains are secured by miners or validators who solve complex mathematical puzzles or reach consensus through consensus algorithms.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are permissioned networks that restrict access and participation to a specific group of participants. They are often used within enterprises or organizations where trust among participants already exists. Private blockchains give more control, privacy, and scalability compared to their public counterparts.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are a hybrid model that combines elements of both public and private blockchains. In a consortium blockchain, a group of organizations forms a consortium and jointly maintains the blockchain network. Consortium blockchains provide a balance between decentralization and controlled access.
To give you deeper idea, here is the table of each blockchain characteristics:
| Characteristic | Public Blockchains | Private Blockchains | Consortium Blockchains |
| Openness | Fully decentralized, distributed network | Restricted access, limited to authorized participants | Restricted access, limited to consortium members |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized, distributed network | Partially decentralized, controlled by a single entity or group | Partially decentralized, controlled by consortium members |
| Transparency | Transparent, all transactions are visible to all participants | Selective transparency, visibility determined by permissions | Selective transparency, visibility determined by consortium rules |
| Trust | Trust is achieved through network consensus and cryptographic algorithms | Trust is established among known participants | Trust is established among consortium members |
| Security | High level of security through decentralization and consensus mechanisms | Relies on the security measures implemented by the controlling entity | Security measures determined by the consortium members |
| Privacy | Limited privacy, transactions are visible to all participants | Enhanced privacy through restricted access and encryption | Privacy measures determined by the consortium members |
| Scalability | Scalability challenges due to the need for consensus among all network participants | Scalable solutions can be implemented due to centralized control | Scalable solutions can be implemented based on the consortium's agreement |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies, DeFi, DApps | Supply chain management, interbank transactions, confidential business networks | Healthcare consortia, supply chain collaborations, industry-specific networks |
Final Thoughts
Blockchain is no longer a future. It’s here already!
With the continuous evolution of blockchain technology, the potential for its application keeps escalating, influencing various sectors in ways that were unimaginable just a few years ago. Blockchain is more than just a technology. It signifies a major transition in our understanding of trust, transparency, and decentralization in the context of the digital universe.


 11 mins read
11 mins read